Lovisenberggata 6, Oslo, Oslo, Norway
Houtribweg 39, Lelystad, Flevoland, The Netherlands
3721 Utrecht Court, Christchurch, England, United Kingdom
Uppsala, Sweden
Stockholm, Sweden
Uppsala, Sweden
Teramo, Abruzzo, Italy
Bettola-Zeloforomagno, Lombardy, Italy
Viale Regina Elena, Rome, Lazio, Italy
Südufer 10, Greifswald, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany
Max-Dohrn-Straße 8, Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Waterloo Road, London Borough of Lambeth, England, United Kingdom
Reigate Road, Reigate and Banstead, England, United Kingdom
Campus-Vienna-Biocenter 191, Vienna, Wien, Austria
Anker Engelunds Vej 1, Stampen, Region Hovedstaden, Denmark
Rue Juliette Wytsman - Juliette Wytsmanstraat 14, Ixelles - Elsene, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale - Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, Belgium

The Project #COHESIVE
| Start: | 1 January 2018 |
| Duration: | 3 Years |
| Domain: | Integrative Activity |
| Keywords: | Common reporting, and signalling procedures, joint platform for sharing surveillance data and their interpretation, incl. risk assessments |
| Contact: | Kitty Maassen (RIVM) |
COHESIVE: One Health Structure In Europe.
The aims of COHESIVE project were to develop sustainable One Health approaches with respect to surveillance, signalling, assessing and controlling zoonoses at the national and regional level within EU countries and across borders.
Working towards a world with less zoonotic disease burden requires collaboration at all levels and between the veterinary and human domain. In some European countries, risk analysis structures to deal with (emerging) zoonoses in an integrated human‐veterinary setting have already been implemented. However, these structures mostly were implemented after experiencing one or more large outbreaks such as BSE in the UK or Q‐fever in The Netherlands. Now, these countries experience the advantages of integrated One Health approaches to deal with (re‐)emerging zoonoses, including AMR and food‐borne zoonoses.
Due to the very different organisation of food production systems, the veterinary and human health domains, both in and between countries, it must be realized that there is no general blue‐print for a OH risk‐analysis structure. In this context, the COHESIVE project was created with the aims to strengthen/improve (structured) collaboration between the human and veterinary domain in the area of risk‐analysis of (emerging) zoonoses in European Member States. It worked to achieve these aims by:
- Stimulating One Health approaches at the national level within EU countries (EJP partner member states) and focusing on strengthening human‐veterinary collaboration by designing common procedures and tools while taking into account similarities and differences between countries. Importantly, the project facilitated creating support for a One Health structure by organizing local workshops with national stakeholders.
- Devising a roadmap towards an EU zoonoses risk‐assessment of risk‐analysis structure. It brought together existing risk analysis and epidemiological tools, skills and facilities that are required for a ‘one‐health’ surveillance over member states borders, including exploration of the use and possible implementation of early warning systems across Europe.
- Designing and testing a common open source platform for the collection and analysis of surveillance and outbreak data on (foodborne) zoonoses. Thus providing IT tools and data that are quickly available, usable and helpful in outbreak situations and for risk assessments. The project focused on establishing, harmonising and improving tools for tracing, WGS and standardized risk assessments. Interoperability with the main data exchange systems at EU level were ensured such as the TESSy platform and the EFSA zoonoses data collection system. The COHESIVE project has now developed a website with guidelines for setting up a One Health Risk Analysis System (OHRAS) for signalling, assessing and controlling zoonoses in European countries: www.ohras.eu.
- Capacity building within and between EU countries at several levels (executive level, communication, policy makers) within the area of zoonotic diseases. Several pilots, within and between countries, tested the developed tools (guidelines for setting‐up a ‘One Health Structure’, risk‐assessment tool, early warning tool, data platform) within country through specific Vet‐Med partnerships. Multiple member states and Vet‐Med partnership assessed the developed tools collectively on combined country surveillance. The COHESIVE project developed guidelines for risk analysis of zoonoses.
Project Outputs and Outcomes
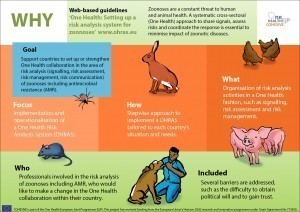
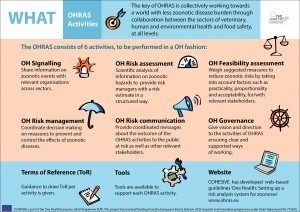
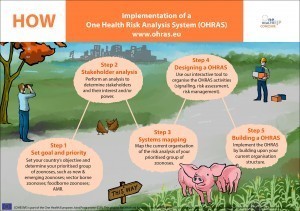
A website with guidelines for setting up a One Health Risk Analysis System (OHRAS) for signalling, assessing and controlling zoonoses and its implementation in European countries (shown in the images at the bottom of this page). The OHRAS has been used by the following countries: Norway, Portugal, Belgium, Denmark, Sweden, Germany and France.
Four IT tools to support outbreaks and risk-based surveillance:
- The COHESIVE Decision Support Tool for One-Health Risk Assessment provides a broad introduction to the field of risk assessment. It classifies different risk assessment approaches against criteria such as timescale, geographical location or level of expertise. It also provides One Health and sector-specific examples of these approaches for further research.
- The COHESIVE Information System (CIS) is database and web-based interface designed to help integrate pathogen information from medical and veterinary sectors, beneficial for outbreak investigation and surveillance.
- FoodChain-Lab web application (FCL Web) enables the reliable tracing of a specific food product along the food supply chain during a foodborne disease incident.
- Shiny Rrisk is a web-based tool for risk assessment using Monte-Carlo Simulation and helps to build quantitative risk models via a user-friendly shiny surface including uncertainty analysis.
More information on COHESIVE outputs can be found here.
Read more about COHESIVE project outcomes and impacts in an interview with Project Leader, Kitty Maassen, published on the RIVM website in October 2022.
Overall, specific COHESIVE resources can be used to facilitate international coordination, improve the efficiency of One Health risk analyses and benefit pandemic disease preparedness.
The COHESIVE project has developed a website with guidelines for setting up a One Health Risk Analysis System (OHRAS) for signalling, assessing and controlling zoonoses in European countries.
For more information, see the three infographics above: Why, What, and How.
Visit the website to access the guidelines: www.ohras.eu.
Project Assets
Mangone, I., Radomski, N., Di Pasquale, A., Santurbano, A., Calistri, P., Cammà, C., Maassen, K. (2021). Refinement of the COHESIVE Information System towards a unified ontology of food terms for the public health organizations. IFOW 2021 Integrated Food Ontology Workshop, September 15-18, 2021, Bolzano Italy. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5645680 & DOI: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2969/paper11-IFOW.pdf
Dewar, R., Gavin, C., McCarthy, C., Taylor, R A., Cook, C., Simons, R R L. (2021). A user-friendly decision support tool to assist one-health risk assessors. One Health, 13, 100266. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100266
Buschhardt, T., Günther, T., Skjerdal, T., Torpdahl, M., Gethmann, J., Filippitzi, M. E., Maassen, C., Jore, S., Ellis-Iversen, J., Filter, M. (2021). A one health glossary to support communication and information exchange between the human health, animal health and food safety sectors. One Health. 13, 100263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100263